VOO and VOOG are two funds offered by Vanguard that attempt to track segments of the S&P 500, though they do this in slightly different ways. VOO gives you broad exposure to the entire S&P 500, making it a simple, low-cost way to capture the performance of the largest US companies. Meanwhile, VOOG focuses on the S&P 500’s fastest-growing stocks, giving you a more growth-oriented portfolio.
Choosing between VOO and VOOG comes down to understanding the type of investor you are and how you want to build your portfolio. Understanding how both funds are built and how they perform will help you determine which is the right option for you.
What Is VOO?
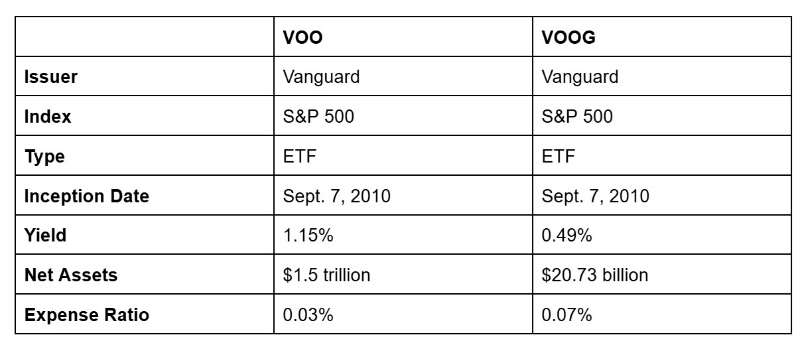
The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) is an exchange traded fund (ETF) that tracks the performance of the S&P 500. It’s a passively managed fund, which helps keep expenses low. At 0.03%, VOO has one of the lowest expense ratios in the industry.
As of Oct. 31, 2025, the fund’s total net assets are $1.5 trillion. And with a turnover rate of just 2.3%, VOO is ideal for buy-and-hold investors. Because VOO aims to track the entire S&P 500, it offers broad diversification across sectors like technology, healthcare, and consumer industrials.
VOO is a popular ETF among investors, and it’s frequently recommended by financial experts. In 2025, ETF inflows reached a new record of $1.22 trillion, with VOO leading all other funds with $7.7 billion in inflows.
However, VOO’s performance is strongly tied to the US economy, meaning an economic downturn or recession can drag down stock prices. The fund also largely relies on large cap stocks, giving you limited exposure to small caps or foreign markets.
What Is VOOG?
The Vanguard S&P 500 Growth ETF (VOOG) tracks the S&P 500 Growth Index, which is a subset of S&P 500 companies classified as “growth” stocks. This index selects companies based on three criteria: sales growth, the ratio of earnings change to price, and momentum. VOOG includes some of the fastest-growth stocks in the S&P 500, but that means it also has fewer holdings than VOO—217 in total compared to VOO's 505.
VOOG has an expense ratio of 0.07%—which is still considered very low, especially when compared to other large growth funds. For example, out of 199 funds, the average expense ratio is 0.37%. Because VOOG can only hold growth companies, it requires more frequent rebalancing.
VOOG tends to be more volatile than VOO since it’s more sensitive to big cap growth stock swings. But that means it may also offer a higher upside during bull markets, especially when tech stocks are performing well. In general, VOOG appeals to investors who want long-term growth potential and are comfortable with higher volatility.
More information here:
How Do You Evaluate and Compare Mutual Funds and Exchange Traded Funds?
VOO vs. VOOG: A Side-by-Side Comparison
The following table provides an overview of how VOO and VOOG compare, as of October 31, 2025:
Average Earnings
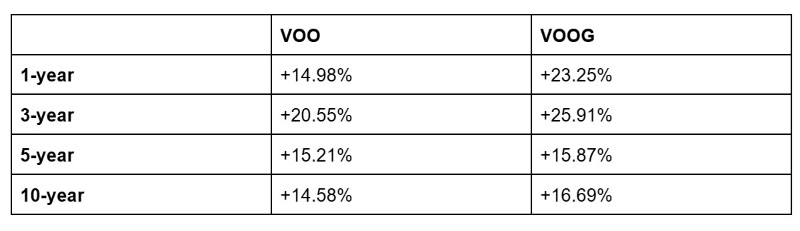
Here’s how the average earnings of VOO and VOOG compare, as of December 17, 2025:
Similarities and Differences
While both funds come from Vanguard and pull from the S&P 500, they behave differently because of the way each index is built and the sectors they emphasize.
Similarities
- S&P 500 indexes: Though the focus differs, both funds draw from the same large cap US companies.
- Passively managed ETFs: Both funds are passively managed, which keeps the costs and turnover relatively low.
- Long-term investing: Both are built for long-term investing, not short-term gains or income.
Differences
- Investing style: While VOO focuses on broad market investing, VOOG focuses solely on growth-oriented companies. VOO owns the entire S&P 500, while VOOG holds around 217 companies.
- Volatility: VOO is less volatile because it provides exposure to a combination of growth and value companies. In comparison, VOOG tends to experience sharper downturns and rebounds than VOO.
- Sector exposure: VOO is broadly diversified across sectors like technology, financials, healthcare, consumer staples, and industrials. Meanwhile, VOOG is heavily weighted toward tech-adjacent sectors like information technology, communication services, and consumer discretionary.
- Turnover: Because the S&P 500 rarely changes, VOO’s turnover is 2.3%. VOOG requires more frequent adjustments as companies shift between growth and value categories.
- Average returns: While both funds have delivered strong returns, VOOG consistently outperforms VOO when it comes to average returns.
More information here:
The Bottom Line
VOO and VOOG are both strong choices for long-term investors, but they serve different purposes. VOO is best-suited for investors who want broad market exposure, low risk, and minimal fees. VOOG may appeal to investors who want the potential for higher returns and are comfortable with the volatility that comes with a more concentrated portfolio.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your goals and risk tolerance. And keep in mind, you don’t necessarily have to choose—many investors hold both funds, using VOO for the majority of their portfolio and adding VOOG for additional growth potential.
Which S&P 500 fund do you prefer? Do you like more volatility, or are you looking for more risk? Or is there a non-Vanguard S&P 500 index that you like the best?
